| Show all terms |
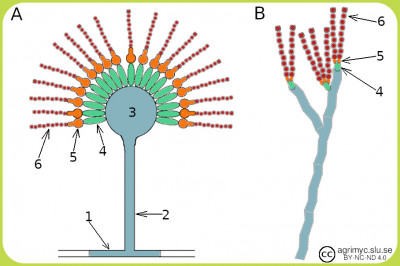
ConidiophoreThe figure shows schematic images of conidiophores of Aspergillus species (A) and Penicillium species (B). Conidiophores consist of the following components: foot cell (1), stalk (2), vesicle (3), metula (4), phialid (5) and conidia (6). Some variation occurs between different species and e.g. A. fumigatus lacks metula. - Click on the image to enlarge it. IntroductionConidiophore is a type of propagating body that produces conidiospores (or conidia) and they are found in e.g. sac fungi (phylum Ascomycota). The conidia are unicellular or multicellular and are formed by lacing from phialid cells (or fialids). This form of reproduction takes place asexually. If the conditions are the right ones, then the conidia form the so-called germination tubes, which grow and form hyphae and fungal mycelium. Updated: 2023-02-08. |